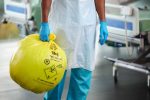
In healthcare facilities, the proper management and disposal of medical waste are important in protecting public health and the environment. Different types of waste require specific handling, segregation, and disposal methods. Clinical waste can be separated into infectious waste, commonly disposed of in orange and yellow clinical waste bags; and cytotoxic waste, disposed of in purple waste bags. Their usage in healthcare means that implementation is crucial in controlling the risk of exposure to infection.
Clinical Waste Streams
- Infectious Waste
Infectious waste, sometimes known as contaminated waste, refers to waste that has the potential to cause infection. It includes materials contaminated with blood, bodily fluids, or other infectious materials that are often soiled by patients with infections and infectious diseases. Predominately, this waste is disposed of in orange clinical waste bags, but where waste is contaminated by chemicals and pharmaceuticals, they should be disposed of in yellow clinical waste bags. Both waste streams involve different methods of disposal, which in the UK involves alternative treatment, or incineration at licensed facilities.
- Cytotoxic & Cytostatic Waste
Cytotoxic and cytostatic waste refers to waste generated from the handling, preparation, and administration of cytotoxic drugs. This waste stream requires special handling and disposal due to its hazardous nature. Purple clinical waste bags, or yellow clinical bags with a purple stripe, are used to segregate cytotoxic and cytostatic waste, which is then disposed of through high-temperature incineration.
Infectious Waste
Orange Waste Stream
Orange clinical waste bags are widely used in healthcare settings to handle and dispose of infectious waste. The infectious waste stream includes any waste that is contaminated by pathogens such as bacteria or viruses that can cause infection. The purpose of segregating this waste is to minimise the amount of people exposed to infection, and if not managed correctly, can pose a risk of infection to healthcare workers, patients, and the public.
Clinical waste bags are located in various areas of the hospital, including wards, bays, and clinics. They are for the collection and disposal of items such as:
- Used gloves, masks, and aprons
- Soiled dressings and bandages
- Infectious swabs and laboratory specimens
- Sharps waste (e.g., needles, syringes, and scalpels) placed in sharps containers
- Any other materials that have been in contact with blood, bodily fluids from a patient with an infection.
Disposing of Orange Waste Bags
In most cases, orange clinical waste bags are incinerated at specialised facilities. Incineration is a highly effective method for destroying pathogens and reducing the volume of waste. It also prevents the release of hazardous substances into the environment.
Yellow Waste Stream
Yellow clinical waste bags are specifically designated for the disposal of chemically and pharmaceutically contaminated waste. This waste stream includes materials that are potentially hazardous due to their chemical properties, such as toxicity or flammability, as well as pharmaceutical contaminated waste. This stream is also used in instances where there are cases of high-level disease and infections.
This waste stream is implemented within healthcare settings where chemical or pharmaceutical waste is generated, such as pharmacies, research laboratories, and certain clinical areas. The following items are typically placed in yellow clinical waste bags:
- Infectious swabs and dressings that are contaminated with topical medicines
- Tissues and paper towels contaminated with chemicals
- Sharps contaminated with medicines or chemicals
Disposal Methods & Cost of Disposal
The disposal methods for yellow clinical waste bags differ from orange bags. Chemically and pharmaceutically contaminated waste is often treated through processes such as high-temperature incineration. These methods aim to render the waste safe, minimising environmental and public health risks.
The cost of clinical waste disposal varies depending on factors such as the volume of waste generated, local regulations, and the waste management company. Incineration is more expensive than other disposal methods due to the specialised equipment and processes involved.
In the UK, the transportation of clinical waste is subject to the regulations set forth in the Carriage of Dangerous Goods and Use of Transportable Pressure Equipment (CDG) Regulations. These regulations are the local implementation of the Agreement Concerning the Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) regulations. Both regulations outline and define requirements for transport of dangerous or hazardous materials, including clinical waste. Waste management companies handling the transportation of clinical waste must be registered and compliant with these regulations to ensure the safety of those involved and the general public and to fulfil their legal requirements.
In the context of clinical waste management in the UK, alternative treatment of waste refers to the process of treating or disposing of clinical waste through methods other than incineration. It involves using alternative technologies and processes that are considered more environmentally friendly and sustainable.
Traditionally, clinical waste was predominantly disposed of through high-temperature incineration. However, in recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on exploring alternative treatment options to reduce the environmental impact of waste management.
The objective of alternative treatment methods is to minimise the release of harmful emissions, reduce energy consumption, and optimise resource recovery where possible. The UK’s waste management regulations and guidelines outline specific requirements and standards for the treatment and disposal of clinical waste, including the use of alternative treatment methods. These measures aim to protect public health and the environment while promoting sustainable waste management practices.
Optimising Waste Management in the healthcare can have numerous benefits, including cost savings, environmental sustainability, and improved overall efficiency.